Understanding the Crankshaft of an Engine
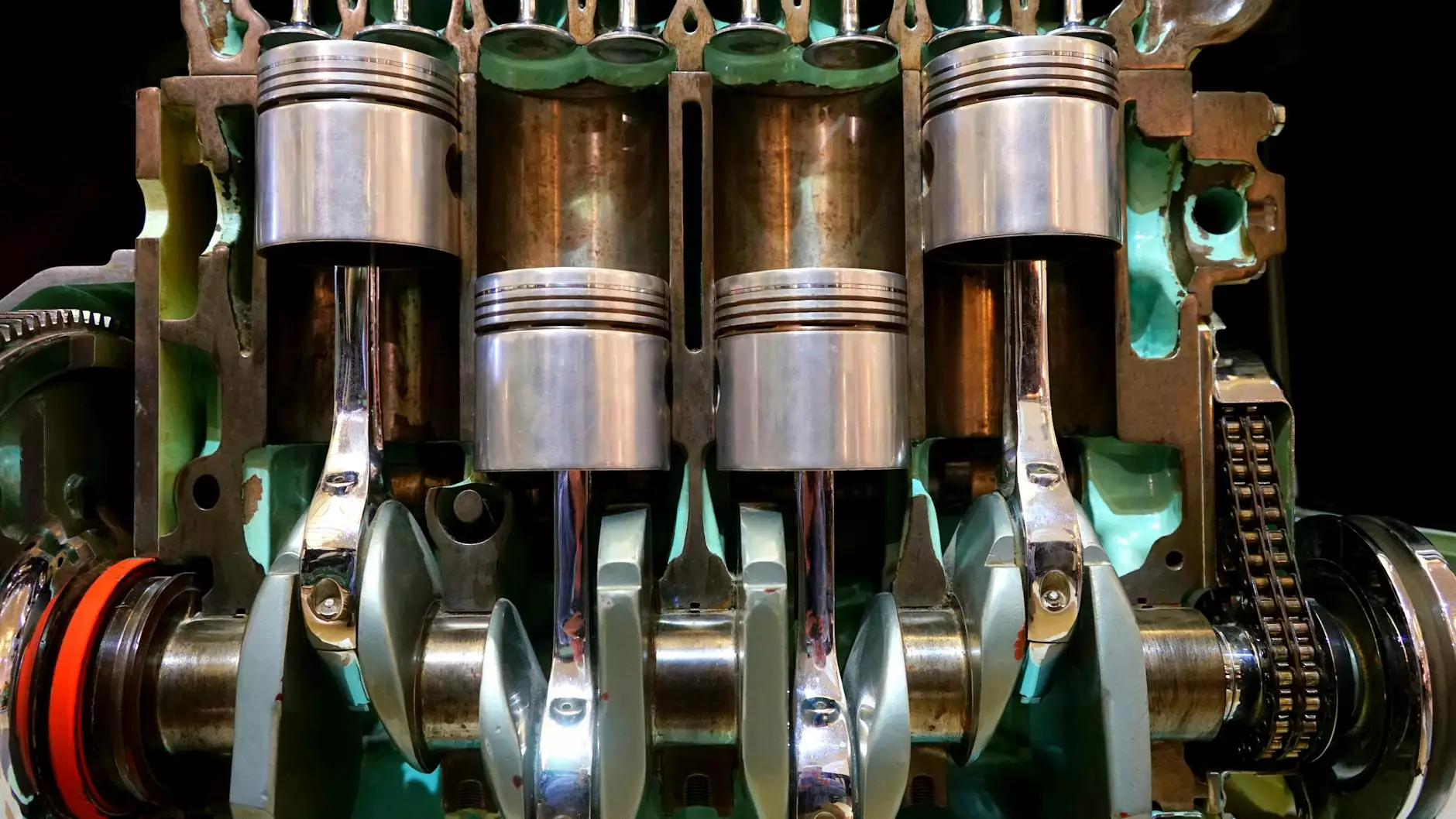
The Crankshaft of an Engine: An Overview
The crankshaft of an engine plays a pivotal role in converting linear motion into rotational motion, allowing the engine to function efficiently. It is a heavy-duty component fabricated from high-strength steel or iron, designed to withstand the enormous pressures and stresses encountered during operation. In this article, we will delve deep into the functioning, significance, and maintenance of crankshafts, particularly in diesel engines.
Key Functions of the Crankshaft
The crankshaft fulfills several essential functions:
- Converts Linear Motion: The crankshaft converts the up-and-down motion of the pistons into rotational motion, which ultimately drives the vehicle or powers machinery.
- Balances Engine Forces: It helps in balancing forces created by the rotation of engine components, contributing to the overall stability of the engine.
- Distributes Power: The crankshaft aids in distributing power to various engine components through connected systems such as the timing belt.
- Facilitates Engine Cooling: By turning, it helps circulate oil, ensuring all engine parts remain lubricated and cool.
The Crankshaft in Diesel Engines
In diesel engines, the crankshaft is even more critical due to the unique characteristics of diesel combustion. Diesel engines operate at higher compression ratios than their gasoline counterparts, resulting in greater stress on the crankshaft. Here’s why the crankshaft is fundamental in diesel engines:
- Durability: Diesel crankshafts are engineered for durability, supporting high torque outputs.
- Precision Engineering: They must be precisely manufactured to ensure optimal performance and longevity under extreme conditions.
- Vibration Control: Diesel engines typically generate more vibration; thus, crankshafts are designed to dampen these vibrations to protect other engine components.
Components Associated with the Crankshaft
The crankshaft does not work in isolation. It is part of a larger assembly that includes:
- Pistons: These move in sync with the crankshaft to create the rotational force.
- Connecting Rods: They connect the pistons to the crankshaft, transmitting the linear motion.
- Bearings: These minimize friction and wear on the crankshaft as it rotates.
- Timing Gears: They ensure that the crankshaft and camshaft maintain proper timing.
How the Crankshaft Works
The operation of a crankshaft can be broken down into several stages:
- Intake Stroke: As the piston descends, it creates a vacuum that draws in diesel fuel and air.
- Compression Stroke: The piston moves back up, compressing the air and fuel mixture, which is essential for an efficient combustion process.
- Power Stroke: Upon ignition, the explosion forces the piston down, turning the crankshaft.
- Exhaust Stroke: The piston moves back up, expelling the burnt gases, while the crankshaft completes its rotation.
This cycle repeats rapidly, providing power to the engine. The proficiency of this process is crucial to maintaining engine performance and efficiency.
Signs of Crankshaft Issues
As with any engine component, the crankshaft can face various issues, often indicated by specific symptoms:
- Unusual Noises: Knocking or grinding sounds may indicate wear or damage.
- Vibration: Excessive vibration could be a sign of imbalance or misalignment.
- Oil Leaks: Leaking oil can result from worn seals or bearings related to the crankshaft.
- Performance Problems: A decline in engine performance or efficiency may point to underlying crankshaft issues.
Maintaining Your Crankshaft
Proper maintenance can significantly extend the life of your crankshaft. Here are some best practices:
- Regular Oil Changes: Ensuring proper lubrication prevents wear and overheating.
- Monitor Engine Temperature: Overheating can lead to severe damage.
- Routine Inspections: Regularly check for signs of wear, such as unusual noises or vibrations.
- Use Quality Parts: When replacing components, always opt for high-quality parts to ensure compatibility and longevity.
The Future of Crankshaft Technology
As technology advances, new developments in crankshaft design and manufacturing are emerging:
- Materials Science: Innovations in materials, such as lightweight composites, are increasing efficiency while maintaining strength.
- 3D Printing: This technology offers potential for creating complex geometries that traditional manufacturing cannot achieve.
- Enhanced Balancing Technologies: Improved methods for balancing crankshafts can further reduce wear and improve efficiency.
These advancements promise to enhance the performance and reliability of diesel engines significantly.
Conclusion
The crankshaft of an engine is a cornerstone component that significantly influences engine performance, particularly in diesel engines. Understanding its role, maintaining its health, and keeping abreast of technological advancements are vital for anyone invested in the world of diesel engines. By promoting best practices in maintenance and acknowledging the signs of potential issues, we can ensure that our engines remain powerful and efficient.
Learn More About Diesel Engine Parts
For those interested in procuring high-quality diesel engine parts, look no further than client-diesel.com. They specialize in providing a wide range of options, including durable crankshafts and other essential diesel engine components.
© 2023 Client Diesel. All rights reserved.









